Azure Bicep Modules
On previous posts we have been introduced, how to get started, use extension or migrate from ARM templates for azure bicep or how to use in Continuous Delivery/Continuous Deployment, also how to validate Azure Bicep on Pull Requests/Branch protection.
Azure Bicep Modules
On current one I will cover that Azure Bicep enables you to organize deployments into modules. A module is a Bicep file (or an ARM JSON template) that is deployed from another Bicep file. With modules, you improve the readability of your Bicep files by encapsulating complex details of your deployment. You can also easily reuse modules for different deployments. Module is a functionality in Azure Bicep which allows to split a complex template into reusable small parts, not repeating your code and reuse it.
Azure Bicep Modules Sharing
We have three options to share modules:
- template spec
- can be deployed directly from the API, Azure PowerShell, Azure CLI, and the Azure portal, UiFormDefinition
- public modules registry
- only supported by Bicep
- private modules registry
- only supported by Bicep
Module definition
To create module there is not special case word required, any bicep file can be a module.
Template define 3 parameters and use default targetScope value resourceGroup, targetScope specifying the scope of the module deployment.
Target scope possible options:
- resourceGroup
- subscription
- managementGroup
- tenant
When we use multiple deployment scopes in out deployment we could use scope functions
Our bicep module appinsight.bicep example:
@description('Azure region of the deployment')
param location string = resourceGroup().location
@description('Tags to add to the resources')
param tags object = {}
@description('Application Insights resource name')
param applicationInsightsName string
resource applicationInsights 'Microsoft.Insights/components@2020-02-02' = {
name: applicationInsightsName
location: location
tags: tags
kind: 'web'
properties: {
Application_Type: 'web'
DisableIpMasking: false
DisableLocalAuth: false
Flow_Type: 'Bluefield'
ForceCustomerStorageForProfiler: false
ImmediatePurgeDataOn30Days: true
IngestionMode: 'ApplicationInsights'
publicNetworkAccessForIngestion: 'Enabled'
publicNetworkAccessForQuery: 'Disabled'
Request_Source: 'rest'
}
}
output applicationInsightsId string = applicationInsights.id
Using module
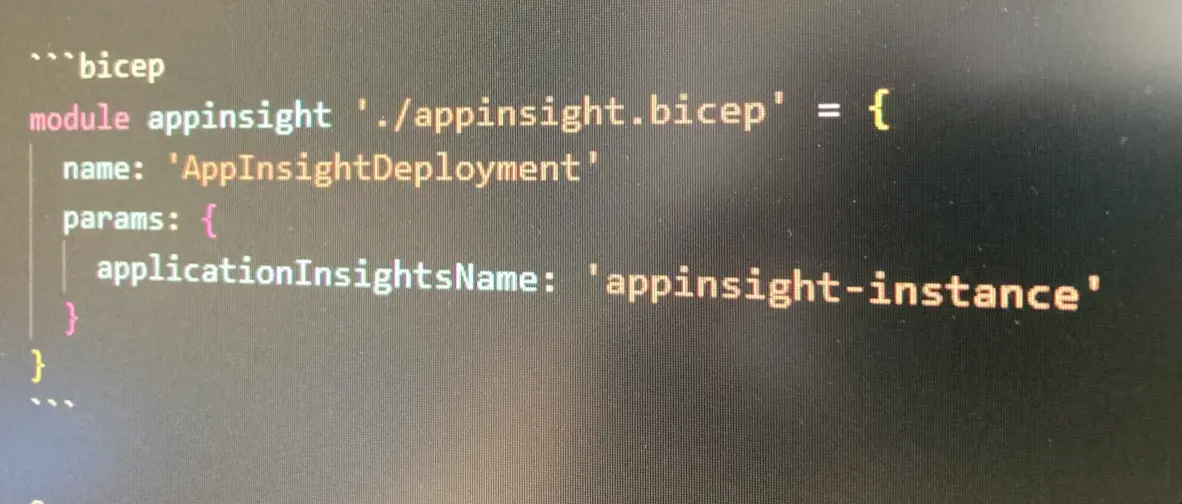
To consume azure bice module we use keyword module and define our own name appinsight with is used for referencing module.
module appinsight './appinsight.bicep' = {
name: 'AppInsightDeployment'
params: {
applicationInsightsName: 'appinsight-instance'
}
}
On current post we cover basic of azure bicep modules, in coming post we will deep dive in more advanced cases.




Comments